Stasis Medical Term: Explained
 3 years ago
By John Lewis Elopre
3 years ago
By John Lewis Elopre

In the realm of medicine, numerous terms hold significance in understanding various physiological and pathological processes. Among these, the term “stasis” emerges as a crucial concept, often intertwined with the intricate workings of the human body. This article delves into the depths of the medical term “stasis,” unraveling its meaning, implications, and relevance within the context of human health and well-being.
Stasis Medical Term: Unveiling the Essence of Stasis
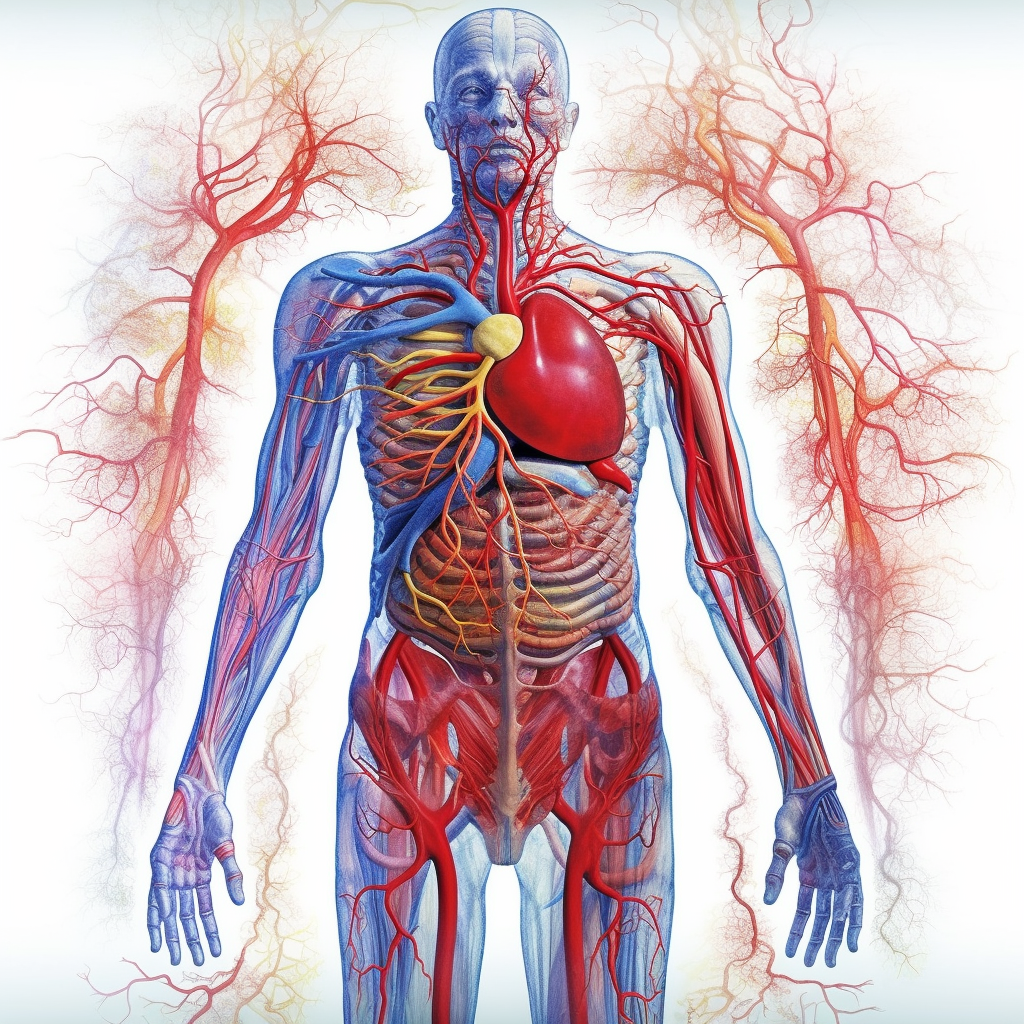
At its core, “stasis” refers to a state of static or stagnant flow, particularly concerning bodily fluids like blood within the circulatory system. The circulatory system, a complex network of blood vessels, is responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and other essential substances throughout the body. Stasis disrupts this harmonious flow, giving rise to a range of potential health issues.
The Dynamics of Circulation
Before delving into the intricacies of stasis, it’s imperative to comprehend the dynamics of circulation. The circulatory system comprises the heart, blood vessels, and blood itself, working in unison to maintain a continuous and balanced flow. The heart acts as a pump, propelling oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to various tissues, while simultaneously pumping oxygen-depleted blood back to the lungs for renewal.
Understanding Stasis in Medical Context
Stasis, in the medical context, occurs when there is an abnormally slow or restricted blood flow within the circulatory system. This sluggish circulation can transpire anywhere in the body, leading to the pooling of blood in specific areas. Such stagnation paves the way for a cascade of complications that can have far-reaching implications on an individual’s health.
Causes and Consequences of Circulatory Stasis
Circulatory stasis can be attributed to a multitude of factors, including sedentary lifestyles, obesity, and certain medical conditions. Prolonged periods of immobility, such as bed rest or extended travel, can also contribute to the development of stasis. The consequences of stasis encompass an elevated risk of blood clots, tissue damage, and impaired delivery of nutrients and oxygen to vital organs.
Detecting Stasis: Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing stasis necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Imaging techniques like Doppler ultrasound and venography play a pivotal role in visualizing blood flow patterns and identifying areas of stagnation. Early detection is paramount, as it enables timely intervention to mitigate potential complications.
Clinical Significance and Implications
The clinical significance of stasis extends beyond its role as a precursor to complications. It can serve as an indicator of an underlying health condition, urging healthcare professionals to delve deeper into a patient’s overall well-being. Addressing stasis promptly can prevent its progression and mitigate the associated risks, enhancing the quality of life for affected individuals.
Preventive Measures to Combat Stasis
Preventing stasis entails adopting proactive measures to promote healthy circulation. Regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and staying hydrated are fundamental steps in preventing stasis. Additionally, avoiding prolonged periods of immobility, especially during long journeys, is crucial in averting the onset of circulatory stagnation.
Treatment Modalities for Stasis Management
The management of stasis involves a multifaceted approach aimed at restoring optimal blood flow and preventing complications. Compression therapy, a widely employed technique, involves wearing specially designed garments to improve circulation and reduce pooling of blood. In more severe cases, medical interventions such as anticoagulants or surgical procedures might be warranted.
Lifestyle Modifications for Circulatory Health
Embracing a lifestyle that promotes circulatory health is paramount in warding off stasis. Engaging in regular exercise routines, maintaining a healthy weight, and refraining from smoking contribute to the overall well-being of the circulatory system. These lifestyle modifications not only prevent stasis but also support cardiovascular health in the long run.
Embracing Mobility: A Stasis-Reducing Approach
Mobility stands as a potent antidote to stasis. Incorporating simple habits such as taking short walks during prolonged periods of sitting or elevating the legs while resting can aid in enhancing blood circulation. These small yet impactful actions promote the steady flow of blood, reducing the likelihood of stasis-related complications.
Addressing Stasis-Related Complications
Left unchecked, stasis can pave the way for various complications, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and venous ulcers. Timely intervention and adherence to medical advice play a pivotal role in mitigating these complications. For instance, individuals at risk of stasis-related blood clots might require blood-thinning medications and regular monitoring.
Stasis in Specific Medical Conditions
Stasis frequently manifests in conjunction with certain medical conditions, further underscoring its clinical significance. Conditions like venous insufficiency, congestive heart failure, and immobility-related issues amplify the risk of stasis. Tailored treatment strategies that address both the underlying condition and stasis are essential for comprehensive patient care.
Future Directions in Stasis Research
The realm of medical research continually strives to unravel the complexities of stasis and its implications. Ongoing studies seek to elucidate novel diagnostic techniques, innovative treatment modalities, and preventive strategies. By delving deeper into the mechanisms of stasis, researchers aim to enhance patient outcomes and refine existing medical practices.
Breaking the Shackles: Overcoming Stasis
Overcoming stasis necessitates a collaborative effort between healthcare providers and individuals alike. Empowering patients with knowledge about stasis and its preventive measures can pave the way for informed decisions and proactive health management. By breaking the shackles of stagnation, individuals can embrace vitality and well-being.
Key Takeaways: Navigating the Currents of Health
In the intricate tapestry of human health, stasis emerges as a critical thread that demands attention and understanding. By comprehending the nuances of stasis, its causes, consequences, and management, individuals can navigate the currents of health with greater insight and vigilance. Embracing a lifestyle that champions circulation and mobility empowers individuals to steer clear of the stagnant waters of stasis and embark on a journey towards optimal well-being.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What exactly is circulatory stasis? Circulatory stasis refers to a slowed or restricted blood flow within the body’s circulatory system, potentially leading to various health complications.
- How does stasis impact overall health? Stasis can contribute to the formation of blood clots, tissue damage, and hindered delivery of oxygen and nutrients to vital organs.
- Can stasis be prevented? Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and avoiding prolonged immobility can help prevent stasis.
- What are some common conditions associated with stasis? Stasis often accompanies conditions like venous insufficiency, congestive heart failure, and immobility-related issues.
- How is stasis diagnosed? Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging techniques like Doppler ultrasound.
Navigating the Complex World of Global Regulatory Affairs in Oncology
In today's fast-paced global pharmaceutical landscape, the regulatory affairs sector plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and market access of oncology drugs. As the demand for innovative cancer therapies continues to grow, understanding the intricacies of global...
3 years agoNavigating the Complex World of Global Regulatory Affairs in Oncology
In today's fast-paced global pharmaceutical landscape, the regulatory affairs sector plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and market access of oncology drugs. As the demand for innovative cancer therapies continues to grow, understanding the intricacies of global...
3 years ago
The Vital Role of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) in Oncology Research
In the world of medical research, ethics play a paramount role. Researchers, especially in fields like oncology, are constantly striving to find innovative solutions and treatments to combat cancer. However, these advancements must be achieved within the boundaries of ethical...
3 years agoThe Vital Role of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) in Oncology Research
In the world of medical research, ethics play a paramount role. Researchers, especially in fields like oncology, are constantly striving to find innovative solutions and treatments to combat cancer. However, these advancements must be achieved within the boundaries of ethical...
3 years ago
Data Privacy and Security in Oncology Trials
In today's digital age, data privacy and security have become paramount concerns across various industries, including healthcare. Within the realm of clinical research, particularly in oncology trials, safeguarding patient data is of utmost importance. This article delves into the critical...
3 years agoData Privacy and Security in Oncology Trials
In today's digital age, data privacy and security have become paramount concerns across various industries, including healthcare. Within the realm of clinical research, particularly in oncology trials, safeguarding patient data is of utmost importance. This article delves into the critical...
3 years ago